
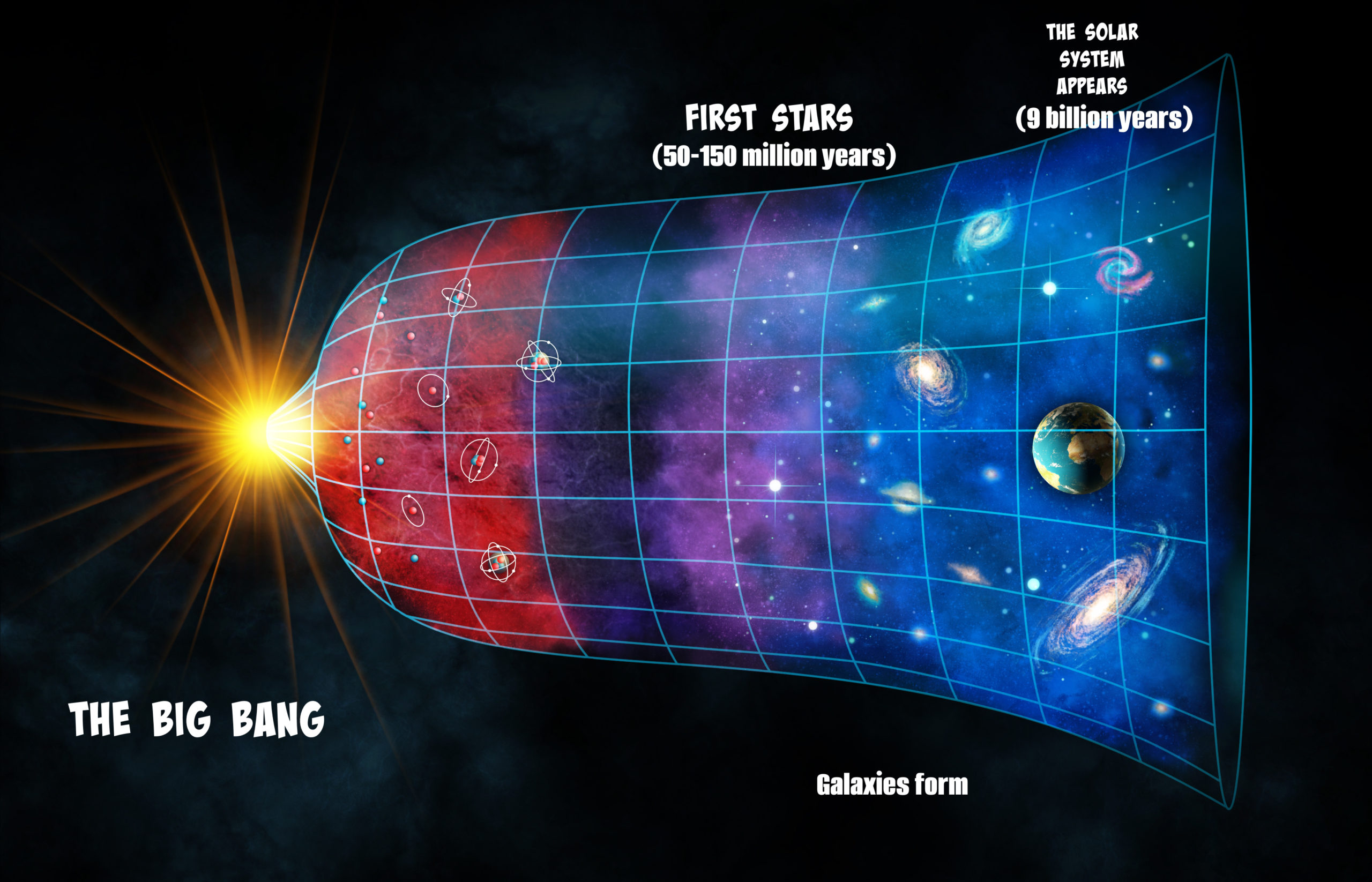
The Big Bang Theory
The big bang theory is one of the most profound theories of how the universe began. It depicts how 13.8 billion years ago the universe began as a tiny, dense, fireball that exploded.
The big bang describes how that the universe began as just a single point, then expanded into where we are today and it is still expanding
“By looking far out into space we are also looking far back into time, back toward the horizon of the universe, back toward the era of the Big Bang.” ― Carl Sagan, Cosmos
The big bang theory also gives us a scientific explanation as to why we are here today. It suggests that through a process of expansion and explosion hydrogen gas was created which led to the formation of stars, and their death ( a supernova) led to the creation of life.
Who discovered the big bang theory?
Georges Lemaître. This idea first appeared in scientific form in 1931, in a paper by Georges Lemaître, a Belgian cosmologist and Catholic priest. Georges Lemaitre discovered the big bang thory by providing a solution or a metric to Einstein's general relativity field equations.
Rival theories
One alternative theory is the Steady State universe.
in the Steady State universe theory it states how the universe is constantly expanding however the density of matter stays the same. This is unlike the big bang theory which says that the density of matter decreases or gets weaker over time as it expands. The Steady state universe theory also supports how the universe had no end or start. Even though it is not as well known or researched cosmological theories. Some scientists still think this is the true meaning of the universe.