
Dark Matter
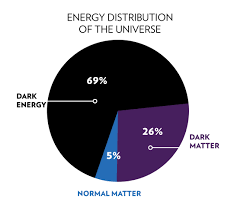
Dark matter is an invisible substance that makes up a large part of the universe's mass. It doesn't emit or interact with light and is detected through its gravitational effects on visible matter, like stars and galaxies, but its composition remains unknown.
Dark matter exceeds regular matter in abundance due to its minimal interaction with other particles during cosmic evolution, forming massive halos around galaxies, while regular matter underwent transformations, leading to its lower quantity and visible structure formation.
"Dark matter and dark energy are two things we measure in the universe that are making things happen, and we have no idea what the cause is." - Neil deGrasse Tyson
Dark matter's presence affects the universe's expansion, galaxy formation, and particle physics. Its nature remains a critical mystery with implications for the cosmos' past, present, and future.
dark energy
Dark energy is a mysterious, evenly distributed form of energy in space that causes the universe to expand at an accelerating rate by generating repulsive gravitational forces. Its nature remains unknown and is a fundamental puzzle in modern cosmology.
Who thoerized dark energy and dark matter?
Fritz Zwicky proposed dark matter in the 1930s for galaxy clusters, and dark energy was discovered in the late 1990s by Perlmutter, Schmidt, and Riess to explain the universe's accelerated expansion, both remaining cosmic mysteries.